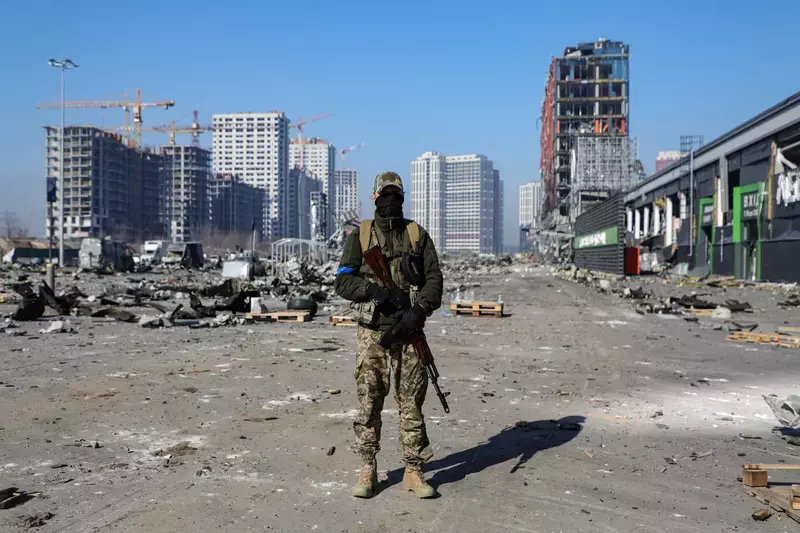
A soldier is pictured outside a shopping mall ruined as a result of a missile strike carried out by Russian troops in the Podilskyi district of Kyiv. (Photo: Yuliia Ovsiannikova / Avalon)
By Aryan D.M
"The pessimist complains about the wind; the optimist expects it to change; the realist adjusts the sails." - Winston Churchill
The Prelude to Conflict
The origins of Russia's invasion of Ukraine in February 2022 are deeply rooted in historical geopolitical tensions.
Ukraine's aspirations for closer ties with Western nations, particularly its expressed interest in NATO membership, have been a source of discontent between the two nations for years.
This geopolitical standoff ultimately boiled over, leading to profound economic consequences.
The situation escalated significantly in 2014 when Russia annexed Crimea, resulting in international condemnation and sanctions.
The subsequent conflict in eastern Ukraine added more complexity to the situation. By the time the invasion occurred in 2022, it was more than a military maneuver; it was a clash of economic powers.
Here's a closer look at the economic prelude to the conflict:
- Geopolitical Context: Ukraine's aspirations for independence and national sovereignty have been a catalyst for the long-standing tension between Russia and Ukraine. Russia's annexation of Crimea in 2014 marked a turning point and was met with severe economic consequences, including sanctions imposed by Western nations. These earlier sanctions set the stage for the more extensive sanctions that followed Russia's invasion in 2022.
- Desire for NATO Membership: Ukraine's desire to join NATO was met with strong opposition from Russia. The possibility of NATO membership raised concerns in Russia, as it could bring NATO closer to its borders, potentially undermining Russian national security. These concerns played a significant role in the conflict and the subsequent economic consequences.
- Conflict in Eastern Ukraine: The ongoing conflict in eastern Ukraine, particularly in the Donbas region, contributed to heightened tensions between Ukraine and Russia. The failure of the Minsk agreements in 2015 to bring a peaceful resolution to the conflict further fueled the animosity between the two countries. The pro-Russian separatist movements in Donetsk and Luhansk complicated the situation, leading to Russia's recognition of these regions in 2022.
Ukraine War Analysis: 600 Days of Conflict

Ukrainian servicemen help to evacuate a wounded soldier at the front line near Bakhmut in the Donetsk region.
Battle Field: Ukraine's Determination Persists Amidst Fatigue
- President Zelenskyy reaffirms Ukraine's commitment to the counteroffensive.
- Ukrainian forces make incremental progress in the south.
- Repelling Russian attacks near Robotyne and Verbove.
- Tragic casualties from Russian shelling in Kherson region.
- Ukraine deploys drones in a targeted attack on Belgorod, damaging an S-400 air defense system.
- Russia's utilization of "glide bombs" in the Kherson region.
- Ongoing Russian efforts to deepen ports for larger ships in occupied Mariupol.
US Aid to Ukraine in the Face of Political Uncertainty
- US President Biden expresses concerns over Republican Party infighting potentially impacting aid to Ukraine.
- British Prime Minister Sunak advocates continued support for Ukraine's fight.
- European Council President Michel supports Ukraine's EU membership by 2030, conditional on reforms.
- Russian blockade affects Ukrainian grain exports.
- International condemnation over the sentencing of journalist Marina Ovsyannikova.
- President Zelenskyy extends an invitation to Pope Francis for a possible visit.
International Support and Depleted Stockpiles
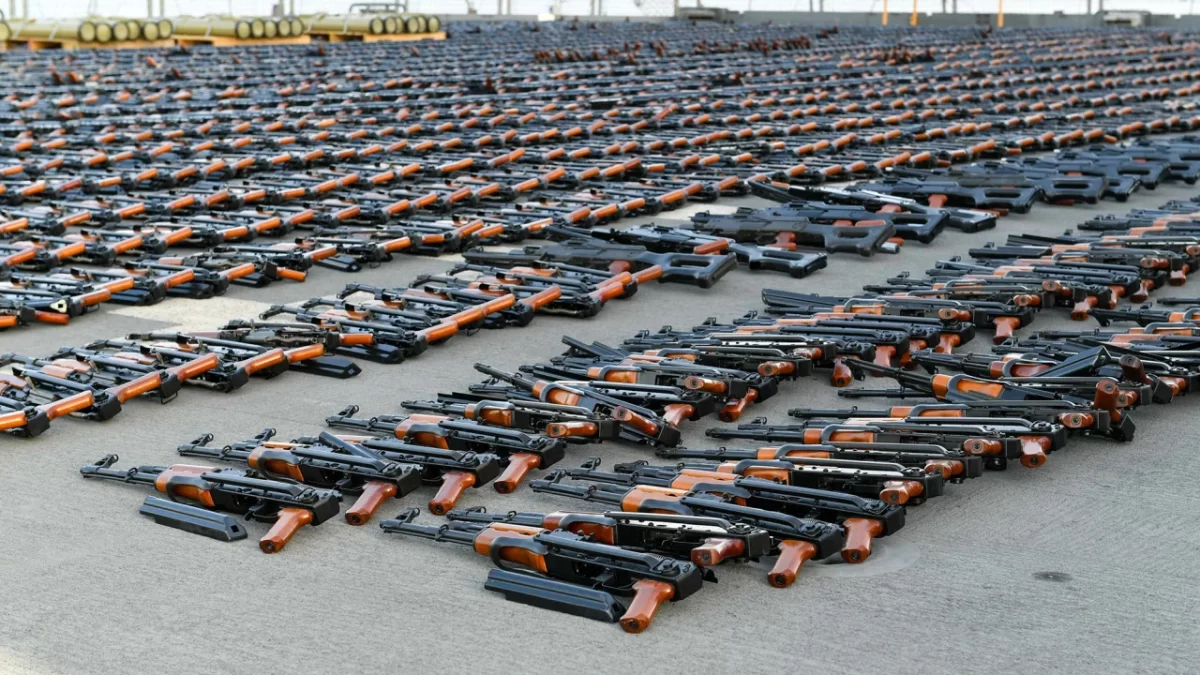

U.S. Central Command supported maritime operations conducted by partner naval forces that resulted in the seizure of advanced weapons during an interdiction in the Gulf of Oman, Jan. 15. (Photo: US Department of Defense)
- The US transfers 1.1 million rounds of small arms ammunition seized from Iran to Ukraine.
- NATO's call for increased arms production due to depletion of stockpiles.
Global Developments
Navalny Lawyers Detained, North Korea's Role, and Ongoing Frontline Fighting
- Russia detains Navalny's lawyers and intensifies pressure on Kremlin critics.
- US alleges North Korea's delivery of military equipment to Russia in exchange for advanced weapon technologies.
- Ongoing battles in Avdiivka as Russia seeks to regain the initiative.
- Putin dismisses claims of damaging a gas pipeline and suggests a western attack on Nord Stream.
- EU leaders demand progress on using frozen Russian assets to aid Ukraine.
- Zelenskyy and Dutch Prime Minister Rutte enhance air defenses and grain export security.
- IOC members Yelena Isinbayeva and Shamil Tarpischev distance themselves from the Russian military and Ukraine invasion.
- IMF meetings in Marrakech affected by disagreements regarding references to Russia's war in Ukraine.
Civilian Casualties in Ukraine 2022-2023: A Grim Assessment
1. Shocking Numbers: 9,614 Civilian Deaths and 17,535 Injuries
- The Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights (OHCHR) reveals the verified statistics of civilian casualties as of September 2023.
- Caution is advised, as the actual figures may be even higher.
2. Impact on Children: A Growing Tragedy
- A harrowing increase of 7% in child casualties in Ukraine from May to August, attributed to a surge in air and drone attacks.
- An overview of child casualties during the 18-month war, totaling over 1,700, with 545 fatalities, including 24 children lost this summer.
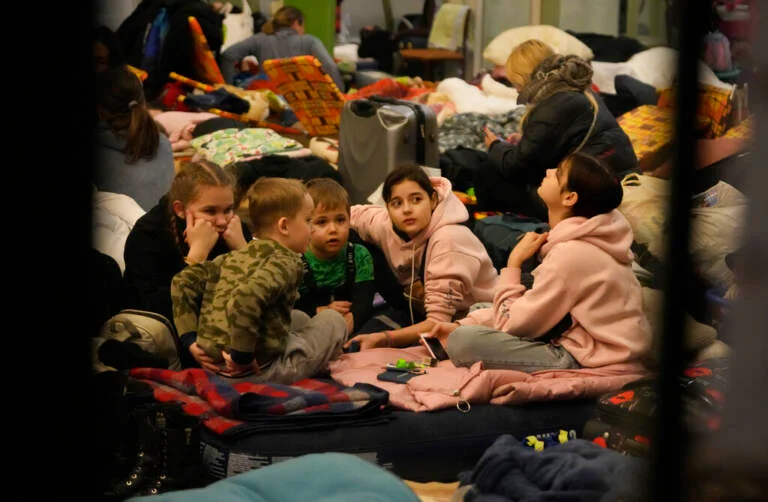

Children, fleeing from Ukraine,play in a shelter designed for women and children at the train station in Przemysl, Poland, Thursday, March 3, 2022. (Photo: AP /Markus Schreiber)
3.Deadliest Month: June 2023
- A closer look at the month of June, the deadliest period in 2023 for Ukrainian children, with 11 deaths and 43 injuries.
- Unveiling a rise in all civilian casualties during the summer, with June recording the highest total civilian casualties of the year at 865.
4. Escalation of Air and Drone Strikes
- Analyzing the surge in air and drone strikes, which increased from 459 in the first four months of the year to 1,432 between May and August.
- Highlighting the alarming statistic that about 95% of these attacks occurred in populated areas.
The Economic Battlefield: Global Ramifications of Russia's Invasion of Ukraine
The economic battlefield resulting from Russia's invasion of Ukraine was multifaceted, impacting various aspects of the global economy.
It went beyond traditional warfare and had far-reaching implications for economies worldwide.
Supply Chain Chaos and Scarcity
Russia's invasion of Ukraine disrupted global supply chains, creating shortages and driving up prices for imported goods.
This was not limited to the conflict zone but had ripple effects across industries and nations. Key points in this economic battlefield include:
- Ukraine as a Key Transport Hub:
Ukraine has historically been a vital transport hub, with its ports playing a significant role in global trade.
The invasion disrupted these critical transportation routes, impacting the delivery of goods worldwide.
Now, let's delve into the profound economic consequences that stemmed from the conflict.
- Security Checks and Border Delays:
Security checks at refugee camps and border crossings added to the supply chain chaos.
Many goods were delayed or halted due to border officials prioritizing refugees over cargo, exacerbating the disruption.
- Inflationary Pressures:
The disruption of supply chains created inflationary pressures in many countries.
Rising prices for imported goods affected the cost of living and posed challenges to economic stability.
Soaring Oil and Gas Prices
Prior to the invasion, energy prices were already on the rise due to various factors, including the lingering effects of the COVID-19 pandemic and supply constraints.
The invasion intensified these trends, particularly in the energy sector:
- Energy Price Trends:
Global energy prices were experiencing an upward trajectory before the invasion.
The price of oil was stable within the range of $80 to $95 per barrel. However, after the invasion, oil prices surged past $100 a barrel.
- Energy Supply Disruptions:
Russia's actions during the invasion made it challenging for European oil marketers and companies to receive energy supplies from Russia.
This was a significant concern given that Russia is the world's second-largest oil producer.
- Gas Price Increases:
Households felt the impact as gas prices rose due to concerns about energy supply disruptions.
This had direct consequences for consumers and added to the global inflationary wave.
The Banking Sector Under Fire
The economic battlefield extended to the banking sector, primarily due to international sanctions targeting Russian banks.
These sanctions had implications for financial institutions globally, leading to a complex financial battleground:
- Sanctions on Russian Banks: Many Western nations imposed sanctions on Russian banks, leading to significant financial losses for these banks and impacting their operations.
- Foreign Banks Operating in Russia: Foreign banks with substantial operations in Russia also faced challenges. Some of these banks experienced losses when they discontinued their Russian subsidiaries.
- Global Banking Repercussions:
The effects of sanctions on Russian banks had a spillover effect on the global banking sector. Smaller banks incurred losses, and the consequences of these measures extended beyond national borders.
Deciphering Russia's Motivations
Understanding the motivations behind Russia's invasion of Ukraine is crucial to assessing its economic impact.
Multiple narratives surround this conflict, reflecting the complex nature of geopolitical tensions.
The Pro-Russian Perspective
The pro-Russian perspective suggests that Russia's actions were driven by a perceived threat to its national security and concerns about Ukraine's alignment with Western powers. This perspective emphasizes the following key points:
- National Security:
Russia viewed Ukraine's desire to join NATO as a direct threat to its national security.
The potential expansion of NATO eastward raised concerns in Russia that it would allow Western powers to encroach on its borders.
- Allegations of Genocide:
Russia claimed that Ukraine was oppressing citizens in separatist regions who were loyal to the Russian government.
Accusations of genocide against its own people further fueled Russia's motivations.
- Non-compliance with Minsk Agreements:
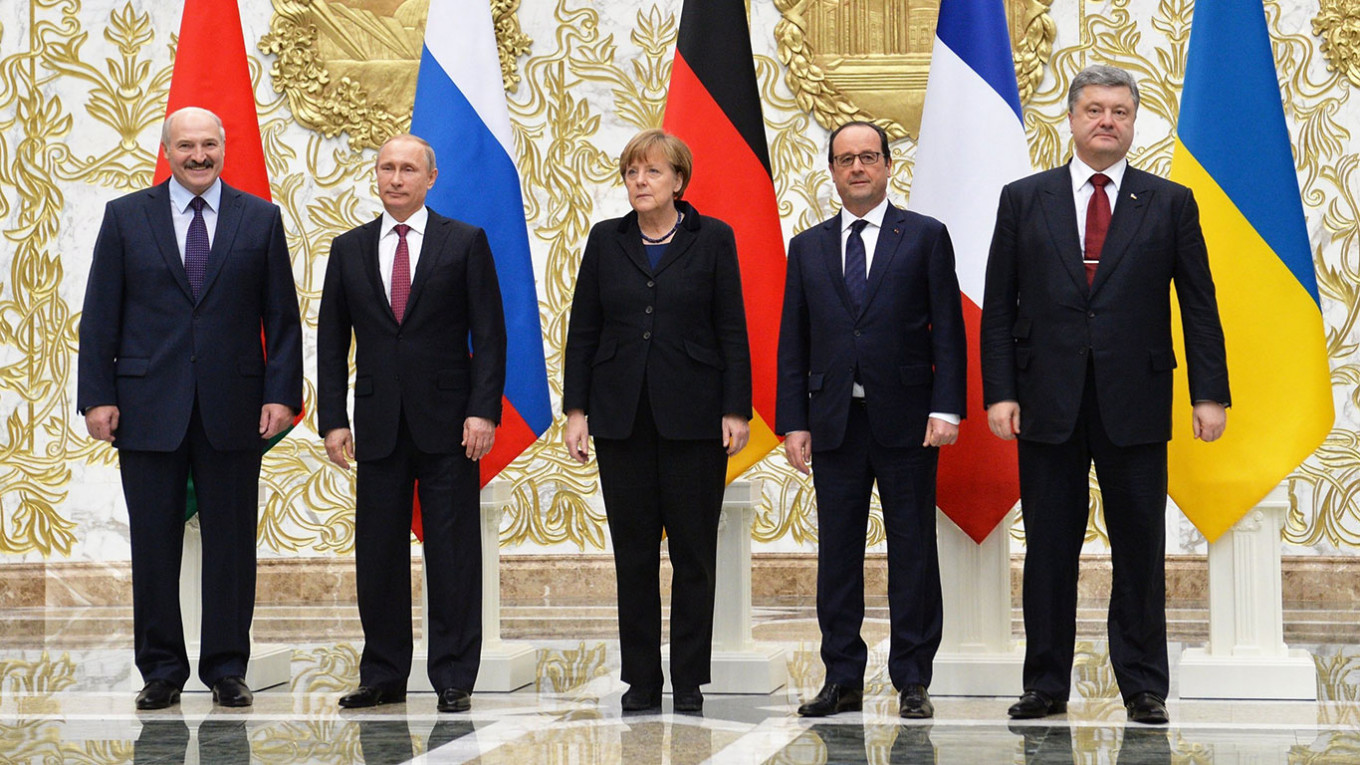

In February 2015, the Minsk II agreements were signed by Belarus' Alexander Lukashenko, Russia's Vladimir Putin, Germany's Angela Merkel, France's Francois Hollande and Ukraine's Petro Poroshenko. (Photo: Kremlin)
Russia argued that Ukraine failed to comply with the Minsk Agreements, which were designed to bring a peaceful resolution to the conflict.
This non-compliance, in Russia's view, justified its actions.
The Pro-Western Perspective
The pro-Western perspective focuses on Ukraine's aspirations for democratic independence and Western alliances, emphasizing the following key factors:
Ukraine's Pursuit of Democracy:
Ukraine's desire for democratic sovereignty and closer ties with the European Union and NATO was a central factor.
The desire for self-determination and alignment with Western values played a significant role.
Russian Opposition to Western Alliances:
Russia's vehement opposition to Ukraine's Western alliance ambitions was viewed as an impediment to Ukraine's pursuit of democracy and independence.
Russia's Response to International Sanctions

(Photo: Shutterstock)
The international community swiftly responded to Russia's invasion with a range of sanctions aimed at crippling the Russian economy.
Russia implemented countermeasures to mitigate the sanctions' impact, which led to an economic trench warfare.
Diversifying Energy Payments
In response to sanctions, Russia demanded Rubles instead of US dollars for energy exports.
This strategic move aimed to strengthen the Ruble and insulate Russia's economy from the negative effects of dollar-based financial sanctions.
Pegging the Ruble to Gold
Russia took the unprecedented step of pegging the Ruble to gold.
This bold decision was intended to challenge the dominance of the US dollar as the ultimate reserve currency and mitigate the effects of multilateral financial sanctions.
Export Bans
Russia implemented a series of export bans, targeting over 200 products across various industries.
These bans were strategic decisions designed to safeguard Russia's economic interests, affecting sectors such as agriculture, technology, and machinery.
Strengthening Economic Ties with Non-Western Allies

Russian President Vladimir Putin speaks with Chinese President Xi Jinping after the meeting in narrow format of the 22nd Shanghai Cooperation Organisation Heads of State Council (SCO-HSC) Summit, in Samarkand, Uzbekistan, Sept. 16, 2022. (Photo: Sergei Bobylev, Sputnik/Kremlin Pool,EPA-EFE)
To counter the economic impact of sanctions, Russia focused on strengthening economic ties with non-Western allies, notably China. Trade agreements and currency swaps played a vital role in these efforts.
Unmasking a Climate Catastrophe: Russia's War in Ukraine, How the War in Ukraine is Pushing Climate to the Brink
In the shadows of the conflict in Ukraine lies a climate catastrophe of unparalleled magnitude.
A recent report has unveiled a shocking environmental crisis borne out of Russia's actions in Ukraine.
This analysis delves into the chilling implications of the war on our planet, underscoring the pressing need to address these dire consequences.
Carbon Assessment:
Carbon experts conducted an alarming evaluation of the first year of the Ukraine conflict, which began in February 2022.
Their findings exposed a grim reality: the war unleashed an unprecedented 120 million metric tons of planet-heating pollution during this period.
This amount is equivalent to the annual emissions of an entire nation or the exhaust of nearly 27 million gas-powered cars on the road for a year.
Unprecedented Mapping:
Lennard de Klerk, the lead author of the report and a specialist in war-related emissions, noted the groundbreaking nature of their work, stating, "It's the first time that the emissions of a war have been mapped on such a comprehensive scale."
The report, titled "Climate Damage Caused by Russia’s War in Ukraine," builds upon an initial assessment presented at the UN COP27 climate conference in November 2022.
Multi-Sourced Data:
The research team harnessed a multitude of sources, including satellites, scientific studies, expert interviews, industry reports, and open-source intelligence, to provide a comprehensive understanding of the climate repercussions of the war.
Their scrutiny extended to pollution stemming directly from warfare, encompassing fuel consumption by tanks, planes, and military equipment, fortification construction, and weapon production.
Additionally, they assessed the aftermath of the war, including fires, destruction, infrastructure reconstruction, and alterations to the European energy mix.

UN secretary-general said the war in Ukraine is putting climate action on the back burner while the planet itself is burning.
War's Direct Emissions:
The report disclosed that nearly 22 million metric tons of planet-heating pollution were directly associated with warfare, constituting almost 20% of the overall emissions attributed to the conflict. However, this estimation may be conservative due to the difficulties in calculating military emissions.
Indirect Emissions:
Indirect emissions emerged from fires caused by shelling, bombings, and explosions, accounting for approximately 15% of total war emissions, totaling nearly 18 million metric tons. Notably, the number of large-scale fires increased substantially during the first year of the war.
Future Climate Impact:
The most significant climate impact, making up nearly half of the pollution generated by the conflict, arises from the post-war reconstruction of damaged infrastructure.
Rebuilding necessitates substantial materials such as cement and concrete, notorious for their high carbon emissions.
Moreover, Russian attacks on energy infrastructure during the conflict have raised the estimated pollution produced during reconstruction.
Beyond Ukraine's Borders:
The report also delves into the effects beyond Ukraine's borders, including the release of methane following the sabotage of Russian gas pipelines Nord Stream 1 and 2.
The shift in Europe's energy mix, influenced by high gas and oil prices, led to increased coal burning, which contributed to heightened planet-heating pollution.
However, the crisis also accelerated the transition to renewable energy sources as countries sought to reduce reliance on Russian fossil fuels.
Airlines and Environmental Costs:
Surprisingly, even airlines felt the environmental impact, as flights were rerouted to avoid Russian and Ukrainian airspace.
The war, therefore, carries substantial consequences in terms of carbon emissions.
Global Consequences:
In the words of James Appathurai, NATO's deputy assistant secretary general for emerging security challenges, "If you look at the environmental costs of what's happening in Ukraine, that war is a catastrophe when it comes to carbon emissions."
The damage, both immediate and long-term, has global implications.
Diminishing Climate Goals:
The report underscores how global commitments to limit warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels are slipping out of reach, raising serious concerns about the world's ability to address climate change effectively.
World Science Under Siege: Unearthing the Profound Impact of the Ukraine War

The Institute for Safety Problems of Nuclear Power Plants has sustained significant damage. (Photo: Anatoly Zagorodny)
The Ukraine-Russia conflict has raged on for over 600 days, wreaking havoc in Eastern Europe.
While much attention has been focused on the political, economic, and social consequences of this war, its effects on science and academia are equally profound.
In this analysis, we delve into the six key scenarios that have globally shaped the world of science during this period of turmoil.
Devastation of Research Infrastructure : “Ukraine's Scientific Foundations Crumble"
The devastating assault on Ukraine has left approximately 27% of research infrastructure in ruins.
Prominent scientific institutions like the Kharkiv Institute of Physics and Technology now lie in disrepair.
Amid rolling blackouts and financial instability, research activities have significantly dwindled, raising questions about the country's scientific revival.
A Pivot Towards Defense: "When Scientists Become Soldiers"

Anti-mobilisation protesters are reportedly being given their draft papers after being arrested. (Photo: EPA-EFE/Maxim Shipenkov)
As research funds were redirected to the military, male researchers, especially those with military experience, found themselves enlisted.
Mandatory mobilization included researchers with degrees in chemistry, biology, and telecommunications.
For both men and women, this shift meant an extended stay in Ukraine.
Now, as mobilization subsides, questions loom about the reintegration of these scientists into research.
The Global Scientific Boycott
"When the World Turns its Back on Russian Science"
Year and half ago, the international scientific community launched a protest against Russia's actions.
Measures included ceasing payments, dissolving collaborative programs, and restricting interactions with Russian institutions.
This widespread "scientific boycott" has led to significant consequences, especially for Russian scientists and institutions.
Russia's Energy Gambit
"Energy Crisis: Russia's Gas Cutoff and Its Ripple Effects"
Russia's response to economic sanctions involved cutting off natural gas supplies to Europe.
This has sent shockwaves through institutions like the German Electron Synchrotron (DESY) and CERN, affecting scientific projects and collaborations. The possibility of a "brain drain" effect adds another layer of uncertainty.
Finding New Homes for Science: "Ukrainian Scientists Abroad: The Search for Support and Opportunity"
Approximately 6,000 Ukrainian scientists now reside abroad, with many in Poland and Germany.
Some continue to contribute remotely to their home institutions. Ad-hoc mobilizations and social media trends have played a crucial role in keeping these researchers engaged in scientific cooperation.
International Efforts for Ukrainian Science: "A Lifeline for Ukrainian Science"
Several research institutions and organizations have stepped up to support Ukrainian scientists and the rebuilding of the scientific community.
Donations, federal research councils, and new funding schemes demonstrate the global community's commitment to nurturing Ukrainian science.
The Debate Over the Science Boycott: "The Divided Stance: The Global Science Community's Boycott Dilemma"
The international scientific community remains divided on the efficacy of the science boycott.
While some argue it punishes unrelated individuals, others support it to varying degrees.
Economic dependencies on Russia further complicate this issue, influencing the direction of Russia's scientific initiatives.
Under the Shadow of crisis: Tech Sector Repercussions in the Russia-Ukraine Crisis
Exploring the Complex Impacts on Technology Companies
The ongoing Russia-Ukraine conflict has far-reaching implications on the technology sector, as a complex web of stringent sanctions, cyber threats, and talent migration unfolds.
European and American tech giants with operations in the region find themselves at the epicenter of this geopolitical storm.
The Tech Sector in Neighboring Nations
Ukraine, along with Poland, Russia, Belarus, Lithuania, Latvia, and Estonia, has been a burgeoning hub for global back offices and technology delivery centers in recent years.
A staggering 44,317 IT service providers across these countries serve 221,102 clients worldwide.
Notably, over 41,861 of these firms are domestic, while 2,456 are subsidiaries of foreign entities.
- A Crisis in Russian IT Firms: Russian IT service providers, numbering 11,049, served 49,445 customers across 112 countries in 2021. The ongoing conflict has caused an existential crisis for these firms, as many global clients are turning away, seeking to sever ties with Russian IT entities.
- Ukraine's Rise and Challenge: Ukraine was rapidly establishing itself as a key player in the global IT landscape. The war's impact on the Ukrainian IT sector is not limited to its domestic firms but also extends to global IT firms with delivery centers in the region.
The Vibrant Ukrainian Tech Scene Pre-Conflict
Before the conflict, Ukraine's technology sector represented over 4% of its GDP, ranking among the fastest-growing markets globally.
Ukrainian IT services, valued at $6.8 billion in 2021, experienced a remarkable 36% year-on-year growth.
Approximately one-fifth of Fortune 500 companies availed themselves of Ukrainian IT services, attracted by favorable governance, tax policies, and a burgeoning tech ecosystem.
- Ukraine's Significance: Ukraine evolved into a significant global tech hub, attracting firms from Western Europe, North America, and Asia. The country housed over 285,000 IT professionals and 4,000 tech companies.
- Diverse IT Expertise: Ukraine's IT sector excels in various industries, from fintech and banking to e-commerce, healthcare, transportation, and education. Although some companies faced disruption, many continue to operate.
- Key Offshore Location: Ukraine ranked high among offshore and near-shore third-party service providers, catering to sectors like banking, retail, automotive, and healthcare.
The Impact of the Conflict on the Technology Sector
Approximately 41,861 domestic firms risk severe business disruption, serving 153,331 customers across 141 countries and 83 sectors.
Many operate in areas affected by war and cyber threats, endangering their business continuity.
Foreign-owned technology firms, numbering 2,456, serve 67,771 customers in 83 sectors.
Their business risks are relatively moderate as operations can be shifted to parent locations, for example, in India. However, the transition process is painful and may disrupt service delivery in the short-to-medium term.
Impacts Rippling Across the Tech Landscape
The war has triggered deep and costly disruptions to supply chains—including the already strained semiconductor value chain as Ukraine and Russia are key producers of neon and palladium. (Photo: Resilinc)
The Russia-Ukraine war affects technology companies in several ways:
1. Escalated Cyber Threats: As the military conflict extends to the cyber realm, companies face an increased risk of frequent cyber-attacks, particularly those with highly integrated global IT systems.
2. Rising Due Diligence: Heightened scrutiny and due-diligence requirements for sanctions result in comprehensive anti-money laundering/know your customer (AML/KYC) processes and lengthy audit trails, affecting business continuity, insurance, and supply chain management.
3. Tech Talent Migration: Ukraine's position as a global tech destination leads to a likely tech talent migration, impacting global tech firms in Europe.
4. Semiconductor Market Disruptions: Ukraine's significant role in the semiconductor market, supplying neon gas and palladium, poses vulnerabilities to the global semiconductor industry.
5. Tech Spending Increase in Europe: The need for expanded sanction reviews, defense, and cybersecurity spending is likely to boost tech spending in Western European countries.
6. Skill Shortages and IT Infrastructure: Firms must invest in managing skill shortages, relocation, and building alternate IT infrastructure, which could be challenging given Ukraine's importance to the sector.
7. Decades to Rebuild: Re-establishing a technology hub as strong as Eastern Europe will take time, impacting start-ups and Fortune 500 companies' digital operations.
Spotlight: The Impact on Healthcare Services
The technology sector in the region serves a multitude of industries, with healthcare organizations accounting for a significant portion of the customer base.
These tech firms serve not only domestic healthcare services but also healthcare firms in other countries, further complicating business disruptions due to the conflict.
Ukraine's : Thriving Amidst Adversity
1. Doomed Predictions:
- Initial predictions painted a dire picture, suggesting that the global technology industry would face an astronomical cost of over 8 trillion dollars as a consequence of the Ukraine war. This projection was based on the expected disruptions and challenges resulting from the conflict.
2. Ukraine's IT Rebound:
- Against the odds, Ukraine's IT industry exhibited remarkable resilience in the face of the conflict. Despite the initial shock of the invasion, over 90% of IT workers in the country returned to work. Notably, the industry managed to achieve record profits in 2022, defying the gloomy forecasts.
3. Global Demand and Talent Gap:
- The global technology sector continues to grapple with a significant and persistent talent gap. While the demand for software developers remains high, the availability of such skilled professionals lags behind. This ongoing gap exerts upward pressure on the rates for software development services.
4. Ukraine's IT Resilience:
- In a surprising turn of events, the Ukrainian software development industry did not experience a substantial reduction in scope as many experts had feared. Furthermore, Fortune 500 companies, which had outsourced IT operations to Ukraine, did not shut down their operations in the region. This resilience underscores the adaptability and stability of Ukraine's IT sector.
5. Ongoing Uncertainty:
The war's impact has given rise to a lingering sense of uncertainty in the technology industry.
Many senior executives are engaged in "what if" discussions and contingency planning to secure remote software development resources outside of Ukraine.
Meanwhile, the demand for software jobs continues to rise, further contributing to the industry's fluid landscape. Additionally, there is a gradual easing of inflation, providing a slightly more stable economic backdrop in 2023.
Summary and Conclusion
In the shadow of the Russia-Ukraine crisis, the world has witnessed the far-reaching impacts on geopolitics, science, technology, the environment, and global economics.
While the conflict has caused disruption and uncertainty, there have been surprising displays of resilience, particularly in Ukraine's IT sector.
The interconnectedness of our global economy and the enduring consequences of this crisis underscore the need for international cooperation and diplomacy.
As the conflict continues, it remains essential for nations to support Ukraine and work together towards global stability, all while bearing in mind the devastating human and environmental costs.
In these challenging times, adaptability, collaboration, and a focus on a better future for all are paramount.


















